VOLUNTEERS
What suspects had done was to answer a local newspaper ad calling for volunteers in a study of the psychological effects of prison life. We wanted to see what the psychological effects were of becoming a prisoner or prison guard. To do this, we decided to set up a simulated prison and then carefully note the effects of this institution on the behavior of all those within its walls.
More than 70 applicants answered our ad and were given diagnostic interviews and personality tests to eliminate candidates with psychological problems, medical disabilities, or a history of crime or drug abuse. Ultimately, we were left with a sample of 24 college students from the U.S. and Canada who happened to be in the Stanford area and wanted to earn $15/day by participating in a study. On all dimensions that we were able to test or observe, they reacted normally.
Our study of prison life began, then, with an average group of healthy, intelligent, middle-class males. These boys were arbitrarily divided into two groups by a flip of the coin. Half were randomly assigned to be guards, the other to be prisoners. It is important to remember that at the beginning of our experiment there were no differences between boys assigned to be a prisoner and boys assigned to be a guard.
Constructing the Experiment
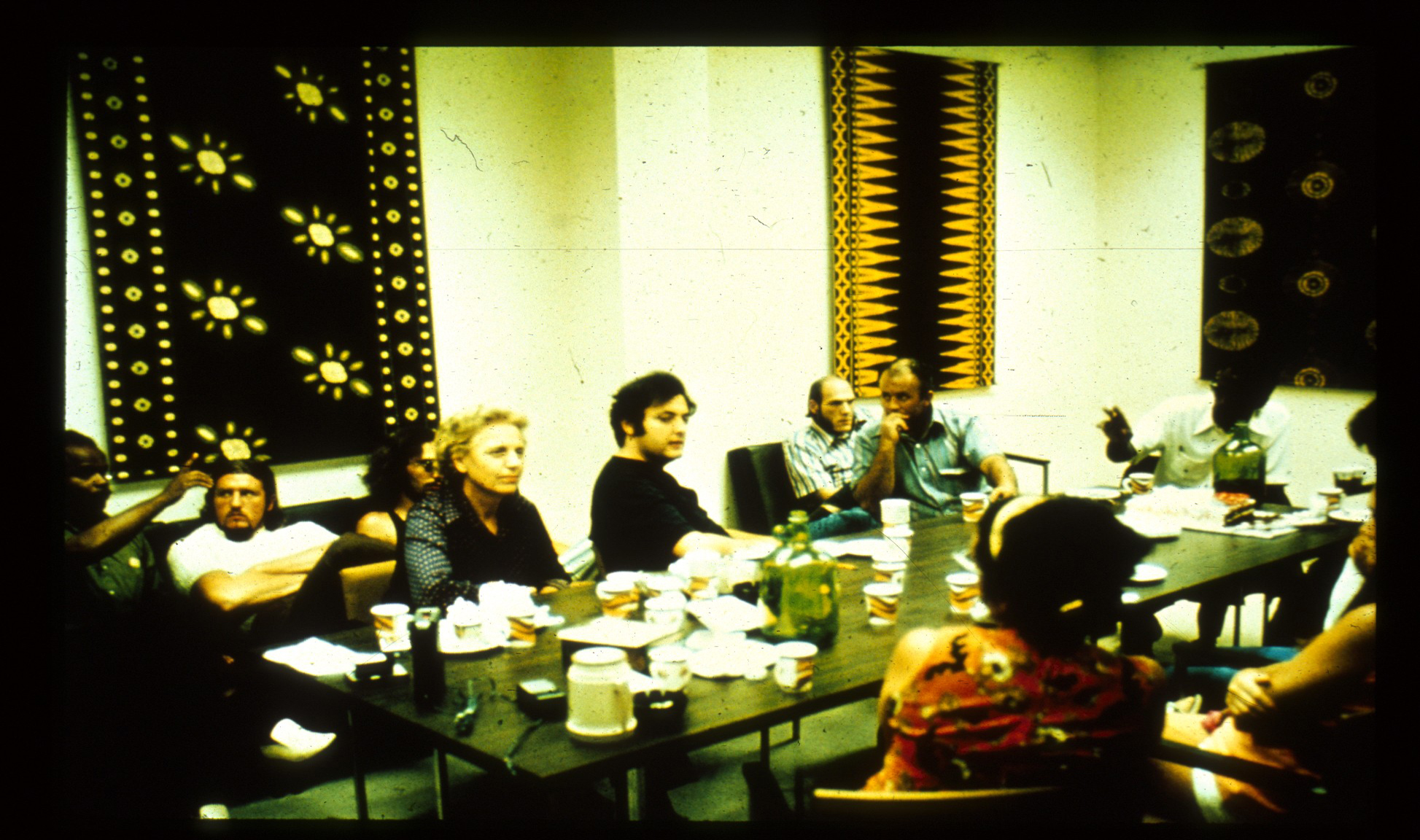
To help us closely simulate a prison environment, we called upon the services of experienced consultants. Foremost among them was a former prisoner who had served nearly seventeen years behind bars. This consultant made us aware of what it was like to be a prisoner. He also introduced us to a number of other ex-convicts and correctional personnel during an earlier Stanford summer school class we co-taught on "The Psychology of Imprisonment."
Our prison was constructed by boarding up each end of a corridor in the basement of Stanford's Psychology Department building. That corridor was "The Yard" and was the only outside place where prisoners were allowed to walk, eat, or exercise, except to go to the toilet down the hallway (which prisoners did blindfolded so as not to know the way out of the prison).
To create prison cells, we took the doors off some laboratory rooms and replaced them with specially made doors with steel bars and cell numbers.
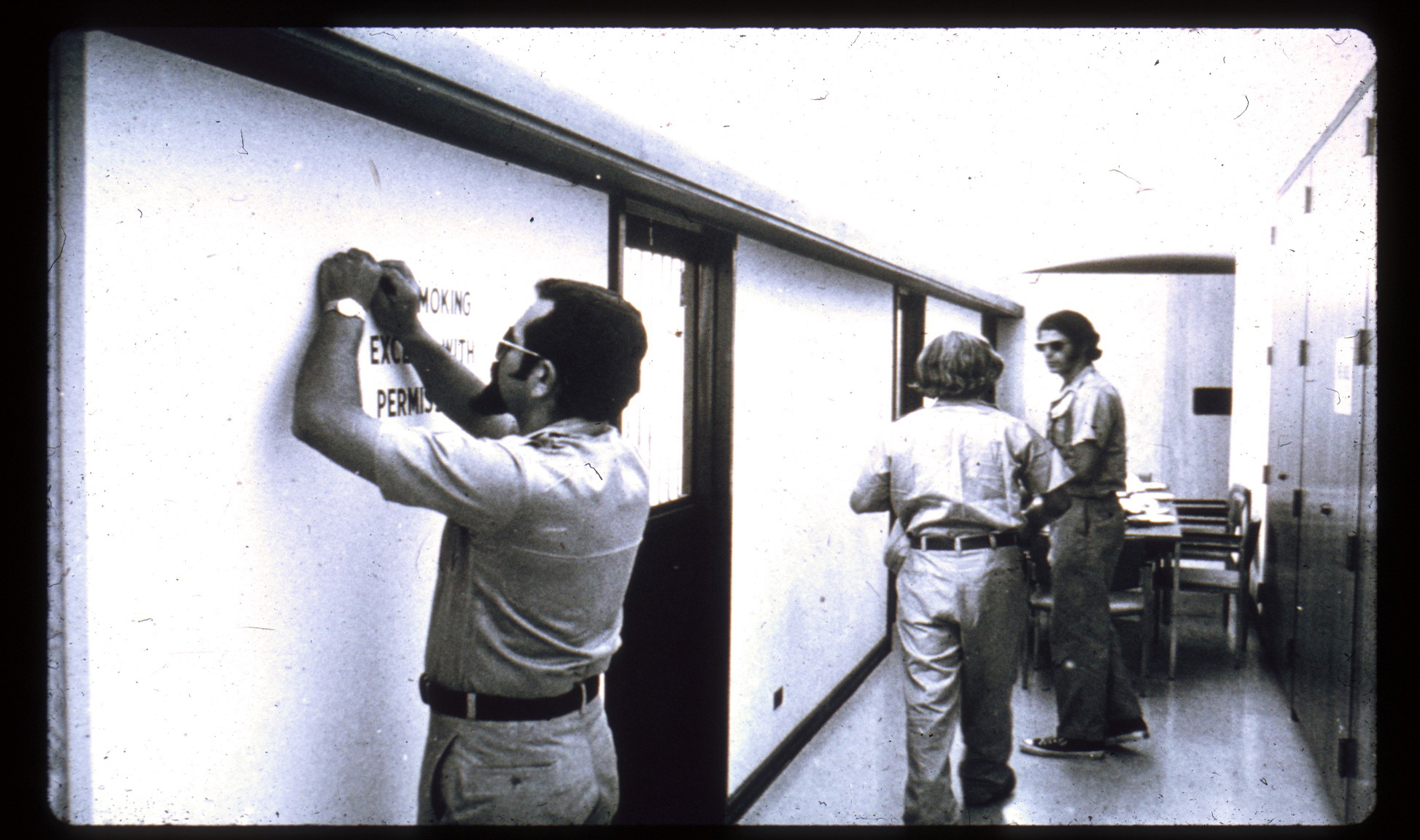


At one end of the hall was a small opening through which we could videotape and record the events that occurred. On the side of the corridor opposite the cells was a small closet which became "The Hole," or solitary confinement. It was dark and very confining, about two feet wide and two feet deep, but tall enough that a "bad prisoner" could stand up.
An intercom system allowed us to secretly bug the cells to monitor what the prisoners discussed, and also to make public announcements to the prisoners. There were no windows or clocks to judge the passage of time, which later resulted in some time-distorting experiences.
With these features in place, our jail was ready to receive its first prisoners, who were waiting in the detention cells of the Palo Alto Police Department.
DISCUSSION:
What are the effects of living in an environment with no clocks, no view of the outside world, and minimal sensory stimulation?


